Overview Table: Background Apps and Their Impact
| Area Affected | Background App Impact | User Benefit of Control |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Slower response, lag | Faster, smoother operation |
| Battery Life | Rapid drain | Longer usage time |
| Internet Data | Hidden data usage | Lower data consumption |
| System Stability | App conflicts | Improved reliability |
| Device Lifespan | Excessive hardware stress | Extended device life |
Stop Unwanted Apps Modern devices are designed to multitask silently. Applications continue working even when they are not visible on the screen, syncing data, checking updates, sending notifications, and consuming system resources. While some background activity is essential for smooth functionality, many Stop Unwanted Apps run unnecessarily, slowing devices, draining batteries, consuming internet data, and reducing overall performance.
For most users, background Stop Unwanted Apps become a hidden problem. The device feels slower, battery life shortens, and data usage increases, yet the cause is not immediately obvious. Understanding how and why apps run in the background, and learning how to control them effectively, is a critical part of digital device maintenance.
This article provides a complete, practical, and in-depth guide on how to stop unwanted apps from running in the background. It blends narrative explanation, analytical reasoning, technical clarity, and a journalistic tone to help users regain control over their devices without relying on external sources.
Unwanted apps running in the background quietly consume system resources long after users believe they are closed. This hidden activity often leads to slower performance, faster battery drain, increased data usage, and unnecessary heat generation. Because these processes operate silently, many users struggle to identify why their device feels sluggish or unstable despite light usage.
As devices become more powerful, applications also become more complex, designed to stay active for updates, syncing, and engagement. While some background activity is essential for functionality and security, a large portion of it provides little real value to the user. Over time, this imbalance creates performance bottlenecks and reduces overall device efficiency.
Learning how to stop unwanted apps from running in the background allows users to take control of their devices instead of reacting to problems after they appear. By managing background activity thoughtfully, it is possible to improve speed, extend battery life, reduce system strain, and create a smoother, more reliable everyday computing experience.
Understanding Background Apps
What Are Background Apps
Background Stop Unwanted Apps are applications that continue to perform tasks even when they are not actively being used. These tasks may include syncing data, checking for updates, tracking location, or sending notifications. While some background activity is essential, many apps operate without offering any immediate value to the user.
Why Apps Run in the Background
Stop Unwanted Apps are often designed to stay active to deliver faster responses, real-time notifications, and seamless user experiences. However, app developers frequently prioritize engagement and data syncing over resource efficiency, leading to excessive background activity.
Difference Between Necessary and Unwanted Background Apps
Essential background apps include system services, security tools, and communication apps that rely on real-time updates. Unwanted background apps typically include games, shopping Stop Unwanted Apps, social media platforms, and pre-installed software that continues running without direct user benefit.
How Background Apps Affect Device Performance
Increased CPU and Memory Usage
Background apps consume processing power and memory, even when idle. When too many Stop Unwanted Apps compete for resources, the system struggles to allocate memory efficiently, resulting in slowdowns and freezing.
Battery Drain and Power Consumption
Continuous background activity forces the processor, network components, and sensors to remain active. This significantly reduces battery life, especially on laptops and mobile devices.
Network and Data Usage
Background Stop Unwanted Apps often sync data silently. Over time, this leads to higher data usage, slower internet speeds, and increased costs for users with limited data plans.
Thermal Stress and Hardware Wear
Sustained background activity increases heat generation. Over time, this heat accelerates hardware wear and can contribute to overheating-related issues.
Identifying Unwanted Background Apps
Monitoring Resource Usage
System task managers provide insights into which Stop Unwanted Apps consume the most CPU, memory, disk, and network resources. Apps consistently using resources without active use are strong candidates for restriction.
Recognizing Behavioral Patterns
If battery drains rapidly when the device is idle, or fans run constantly without heavy usage, background Stop Unwanted Apps are likely responsible.
Evaluating App Necessity
Users should assess whether an app genuinely needs to run continuously. Many Stop Unwanted Apps can function perfectly well when opened manually.
Stopping Background Apps on Windows Laptops
Using Task Manager
The Task Manager allows users to identify running Stop Unwanted Apps and background processes. Closing unnecessary tasks immediately frees system resources, although this is a temporary solution.
Disabling Startup Apps
Many background Stop Unwanted Apps launch automatically at startup. Disabling non-essential startup apps significantly reduces background activity and improves boot times.
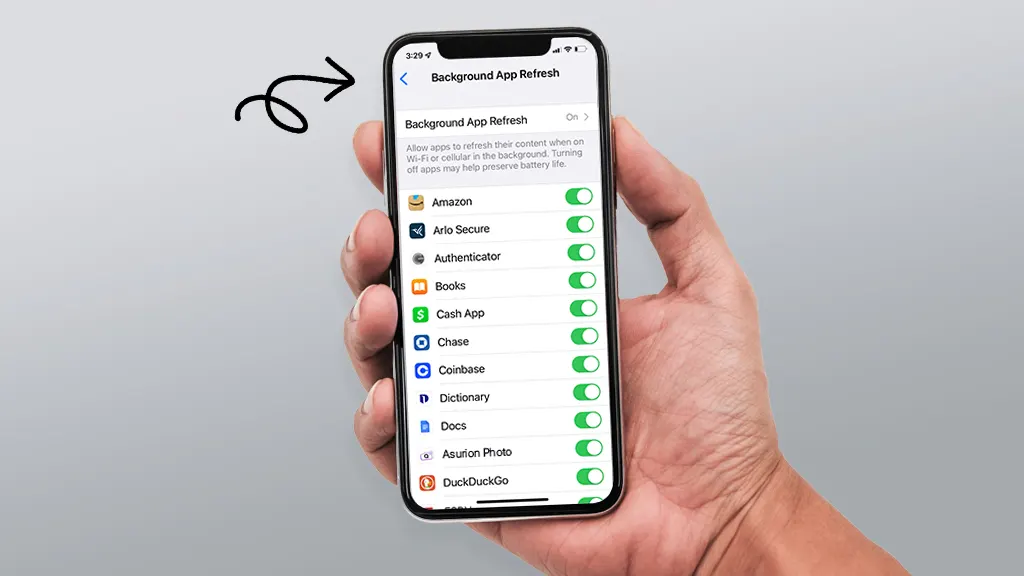
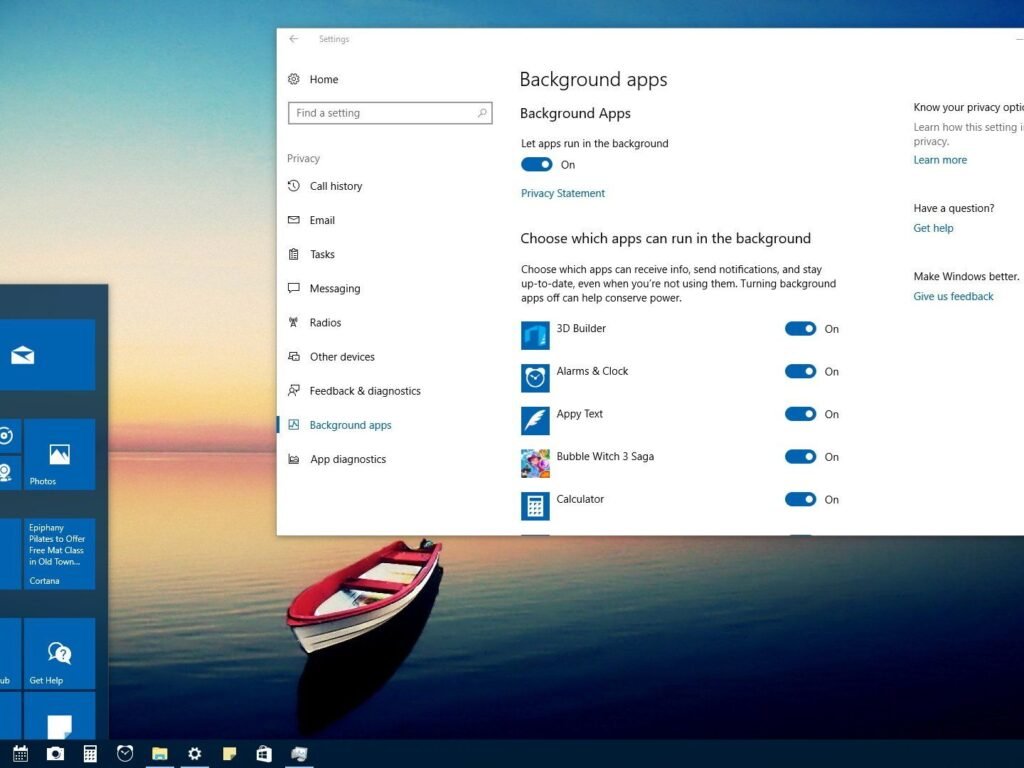
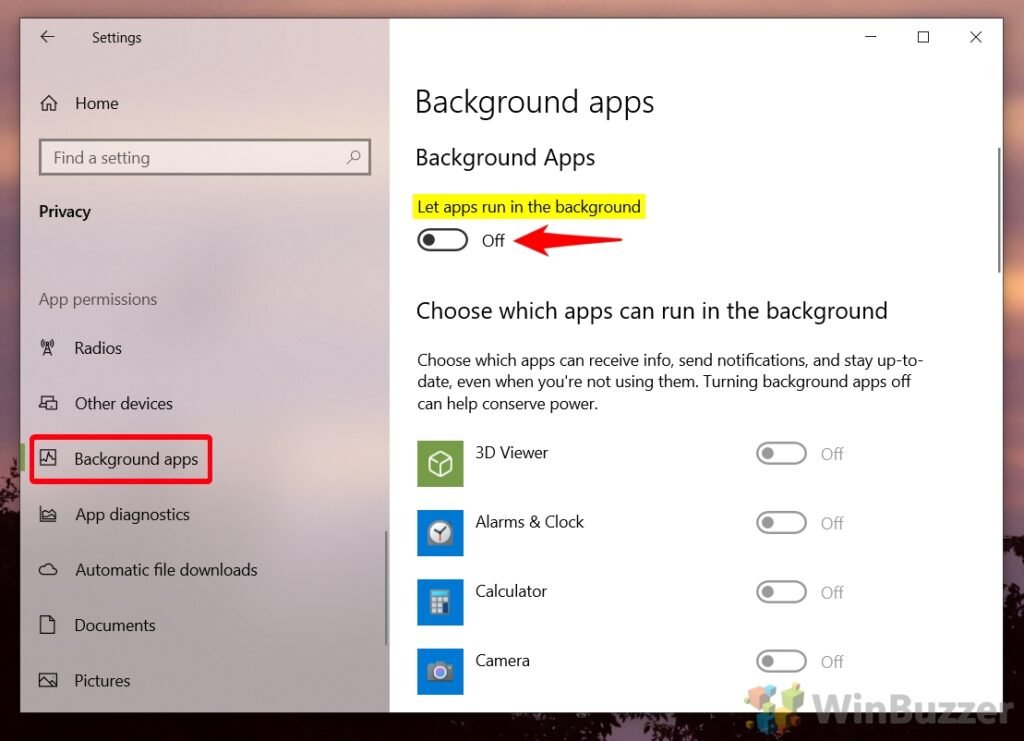
Managing Background App Permissions
System settings allow users to control which Stop Unwanted Apps are permitted to run in the background. Restricting permissions ensures apps only run when actively used.
Uninstalling Unnecessary Software
Pre-installed applications and unused programs often run background services. Removing these apps permanently eliminates their background activity.
Managing Background Apps on macOS
Activity Monitor Usage
The Activity Monitor provides a detailed view of resource consumption. Identifying high-resource background Stop Unwanted Apps helps users take targeted action.
Login Items Management
Apps added to login items start automatically with the system. Removing unnecessary login items prevents background execution from startup.
App Nap and Energy Settings
macOS includes power management features that limit background activity. Ensuring these features are enabled helps reduce unnecessary resource usage.
Controlling Background Apps on Smartphones
Background App Restrictions
Mobile operating systems allow users to restrict background activity for individual Stop Unwanted Apps. This prevents apps from running when not in use.
Battery Optimization Features
Built-in battery optimization tools limit background processes for Stop Unwanted Apps that consume excessive power.
Data Usage Controls
Restricting background data usage prevents Stop Unwanted Apps from consuming internet bandwidth silently.
Browser Extensions and Background Activity
Hidden Resource Consumption
Browser extensions often run background scripts even when the browser is idle. These scripts consume memory and processing power.
Evaluating Extension Necessity
Removing unused or redundant extensions reduces background activity significantly.
Browser Startup and Sync Settings
Browser sync features and startup settings can trigger background activity. Adjusting these settings improves performance.
Managing Background Services and Processes
Understanding System Services
Some background services are essential for system stability. Others are optional and can be disabled safely if not required.
Identifying Non-Critical Services
Services related to third-party software, auto-updaters, and telemetry are often non-essential.
Risks of Disabling Services
Disabling critical services can cause system instability. Changes should be made cautiously and selectively.
Preventing Apps from Restarting Automatically
Auto-Restart Mechanisms
Some Stop Unwanted Apps are designed to restart themselves after being closed. This behavior is often linked to update services or background monitoring.
Adjusting App-Specific Settings
Many Stop Unwanted Apps include internal settings that control background behavior. Disabling auto-sync, notifications, and background refresh reduces activity.
Impact of Background Apps on Security
Increased Attack Surface
More running Stop Unwanted Apps increase the number of potential vulnerabilities. Background apps with internet access may expose sensitive data.
Importance of Regular Updates
Outdated background Stop Unwanted Apps pose security risks. Limiting background activity reduces exposure to vulnerabilities.
Malware Disguised as Background Apps
Malicious software often operates silently in the background. Monitoring unusual activity is essential for detection.
Long-Term Performance Benefits of Limiting Background Apps
Improved System Responsiveness
Reducing background activity frees resources, resulting in faster app launches and smoother multitasking.
Extended Battery Lifespan
Lower power consumption reduces battery wear, extending long-term battery health.
Reduced Heat and Noise
Less background processing decreases heat generation and fan usage.
Creating Healthy App Usage Habits
Installing Apps Selectively
Avoid installing unnecessary Stop Unwanted Apps that add background services.
Reviewing Permissions Regularly
Periodic permission reviews ensure Stop Unwanted Apps do not regain background privileges unnecessarily.
Scheduled Maintenance
Regularly checking startup programs, background permissions, and resource usage prevents gradual performance decline.
Common Myths About Background Apps
Closing Apps Always Saves Battery
Some systems manage background Stop Unwanted Apps efficiently, but unnecessary background activity still consumes resources over time.
System Optimization Tools Are Always Safe
Third-party optimization tools can cause instability. Manual control is often safer and more effective.
When Background Apps Are Necessary
Communication and Security Apps
Messaging, email, and security software require background access to function properly.
Cloud Sync and Backup Services
These services protect data and should be allowed controlled background access.
Signs That Background Apps Are Out of Control
Rapid Battery Drain at Idle
Device Heating Without Active Use
Slow Startup and Shutdown
High Data Usage Without Browsing
Building a Balanced Background App Strategy
The goal is not to disable all background activity but to balance functionality and performance. Users should prioritize essential apps while restricting non-critical ones.
Final Thoughts
Unwanted background Stop Unwanted Apps are one of the most overlooked causes of poor device performance, battery drain, and system instability. While modern operating systems are designed to manage multitasking efficiently, they cannot fully compensate for excessive background activity caused by poorly optimized or unnecessary applications.
By understanding how background Stop Unwanted Apps work, identifying which ones are essential, and actively controlling permissions, startup behavior, and background access, users can dramatically improve device performance. These changes require no advanced technical skills, only awareness and consistency.
Stopping unwanted apps from running in the background is not a one-time fix but an ongoing habit. With regular monitoring and mindful app management, devices remain faster, cooler, more secure, and more reliable over time. This proactive approach transforms everyday technology use into a smoother and more efficient experience, ensuring that devices serve users rather than silently draining their resources.