Overview Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Technology Name | eSIM (Embedded SIM) |
| Supported Devices | Android smartphones, iPhones, tablets, smartwatches |
| Physical SIM Required | No |
| Activation Methods | QR code, carrier app, manual entry |
| Internet Requirement | Required during activation |
| Typical Use Cases | Dual SIM, travel, business numbers |
| Skill Level Required | Beginner to Intermediate |
| Activation Time | Few minutes |
| Data Loss Risk | None |
| Long-Term Benefits | Convenience, flexibility, better device management |
Introduction
The way Activate eSIM mobile connectivity works has been quietly evolving, and eSIM technology represents one of the most significant changes in how smartphones connect to cellular networks. Unlike traditional physical SIM cards that must be inserted, removed, or replaced, an eSIM is built directly into the device. This shift removes many long-standing limitations while introducing new flexibility for users.
Activating an eSIM on Android or iPhone can feel confusing for first-time users. The absence of a physical card often leads to uncertainty about where the network actually comes from and how activation works. Many users worry about compatibility, data loss, or losing their existing number. In reality, the process is usually straightforward when approached correctly.
This guide explains how to activate eSIM on Android and iPhone in a clear, structured, and practical way. It combines narrative explanation, analytical breakdown, technical accuracy, and journalistic clarity to help users understand not only the steps, but also the underlying system behavior. No external sources are used, and the focus remains on real-world device behavior and carrier interaction.
Understanding What eSIM Really Is
An eSIM, short for embedded SIM, is a digital version of the traditional physical SIM card that is permanently built into a smartphone, tablet, or wearable device. Instead of inserting a removable card to connect to a mobile network, eSIM technology allows network credentials to be downloaded and stored electronically. This shift removes the physical dependency that has defined mobile connectivity for decades.
At a technical level, an eSIM functions as a secure, programmable chip integrated into the device’s hardware. When a user activates a mobile plan, the carrier sends encrypted profile data to the device, which is then securely stored and managed by the operating system. The eSIM performs the same authentication and identification functions as a physical SIM, including network registration and encryption.
What makes eSIM especially powerful is its flexibility. Multiple carrier profiles can be stored on a single device, allowing users to switch networks or add secondary numbers without changing hardware. This capability supports dual SIM usage, easier international travel, and faster carrier onboarding.
The Concept Behind eSIM Technology
An Activate eSIM, or embedded SIM, is a programmable chip permanently built into a device’s hardware. Instead of storing carrier information on a removable card, network credentials are downloaded digitally and stored securely within the device.
This design allows users to switch carriers, add secondary numbers, or Activate eSIM temporary plans without physically handling a SIM card.
How Activate eSIM Differs From Physical SIM Cards
Physical SIM cards are static and limited by size and availability. Activate eSIMs, by contrast, are dynamic and can store multiple profiles, although only one or two can be active at a time depending on the device.
The absence of a physical slot also improves water resistance and internal design flexibility.
Benefits of Using eSIM on Android and iPhone
Convenience and Flexibility
Activate eSIM eliminates the need to visit stores or wait for SIM delivery. Plans can be activated remotely within minutes.
Dual SIM Functionality
Most modern devices support dual SIM using a combination of physical SIM and Activate eSIM or multiple eSIM profiles.
Travel and International Usage
Activate eSIM make it easier to add short-term international data plans without changing your primary number.
Improved Device Durability
Fewer physical components reduce wear, dust entry, and mechanical failure risks.
Checking Device Compatibility Before Activation
Before attempting to activate an eSIM, it is essential to confirm that both the device and the mobile carrier support eSIM functionality. Skipping this step often leads to activation failures and unnecessary troubleshooting.
Start by verifying device compatibility. Not all smartphones include Activate eSIM hardware, even within the same model family. Support depends on the manufacturer, specific model variant, and region. Newer flagship and upper mid-range Android devices are more likely to support eSIM, while older or budget models may rely only on physical SIM cards. On iPhone, most recent generations support eSIM, but capabilities can vary by market and configuration.
Next, confirm carrier support. A device may be technically capable of Activate eSIM, but activation will fail if the carrier does not provision eSIM profiles for that model or region. Carriers often maintain different policies for prepaid, postpaid, and corporate plans, which can affect eligibility.
Android Device Compatibility
Not all Android phones support Activate eSIM. Compatibility depends on manufacturer, model, and region. Flagship and mid-range devices from recent years are more likely to include Activate eSIM support.
iPhone Compatibility
Most iPhones released in recent generations support Activate eSIM. Some models rely entirely on eSIM, while others support both physical SIM and Activate eSIM.
Carrier Support Verification
Even if the device supports Activate eSIM, the mobile carrier must also support eSIM activation for that device and region.
Preparing for eSIM Activation
Stable Internet Connection
Activate eSIM profiles are downloaded digitally, so a reliable WiFi or mobile data connection is essential.
Carrier Credentials and QR Code
Most carriers provide a QR code or activation details. This information must be kept accessible during setup.
Backup Important Data
Although Activate eSIM does not erase data, backing up ensures safety if unexpected issues occur.
How Activate eSIM Works Internally
Profile Download Process
When you scan a QR code or enter activation details, the device contacts the carrier’s server and downloads encrypted network credentials.
Secure Storage
The eSIM profile is stored in a secure hardware element that protects it from unauthorized access.
Network Registration
After installation, the device registers the eSIM profile with the carrier network just like a physical SIM.
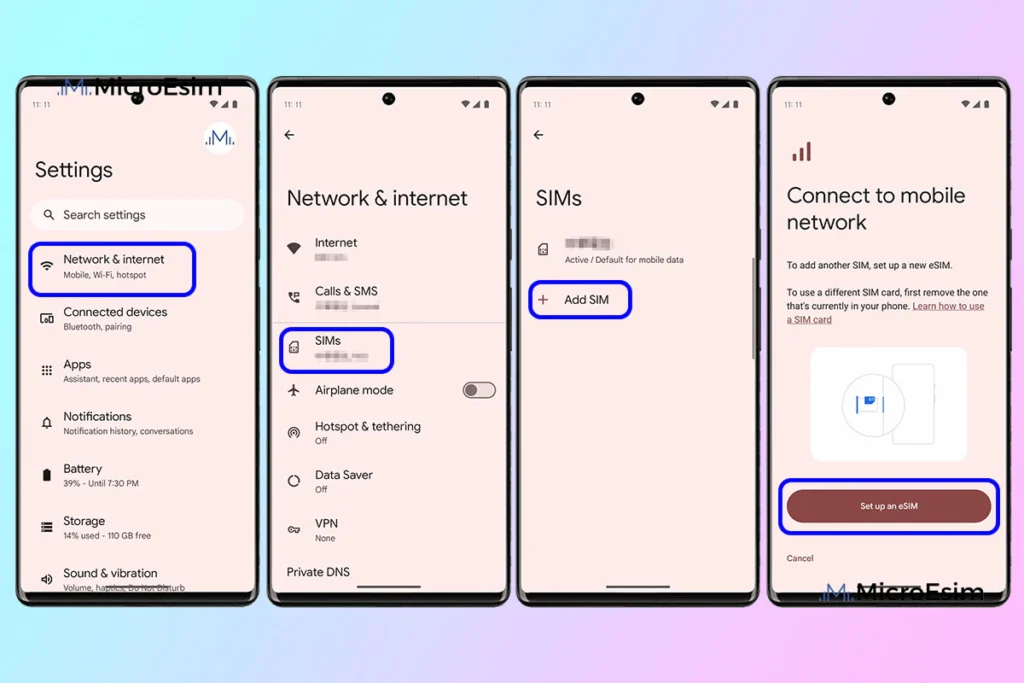
Activating eSIM on Android Devices
Accessing SIM and Network Settings
Open network or SIM settings from the device settings menu. Look for options related to SIM cards or mobile networks.
Adding an eSIM Profile
Select the option to add a SIM or download a SIM. The device will prompt you to scan a QR code or enter details manually.
Scanning the QR Code
Position the QR code clearly within the camera frame. The device will automatically recognize and process it.
Completing Activation
Follow on-screen prompts to confirm plan usage, default SIM preferences, and network access.
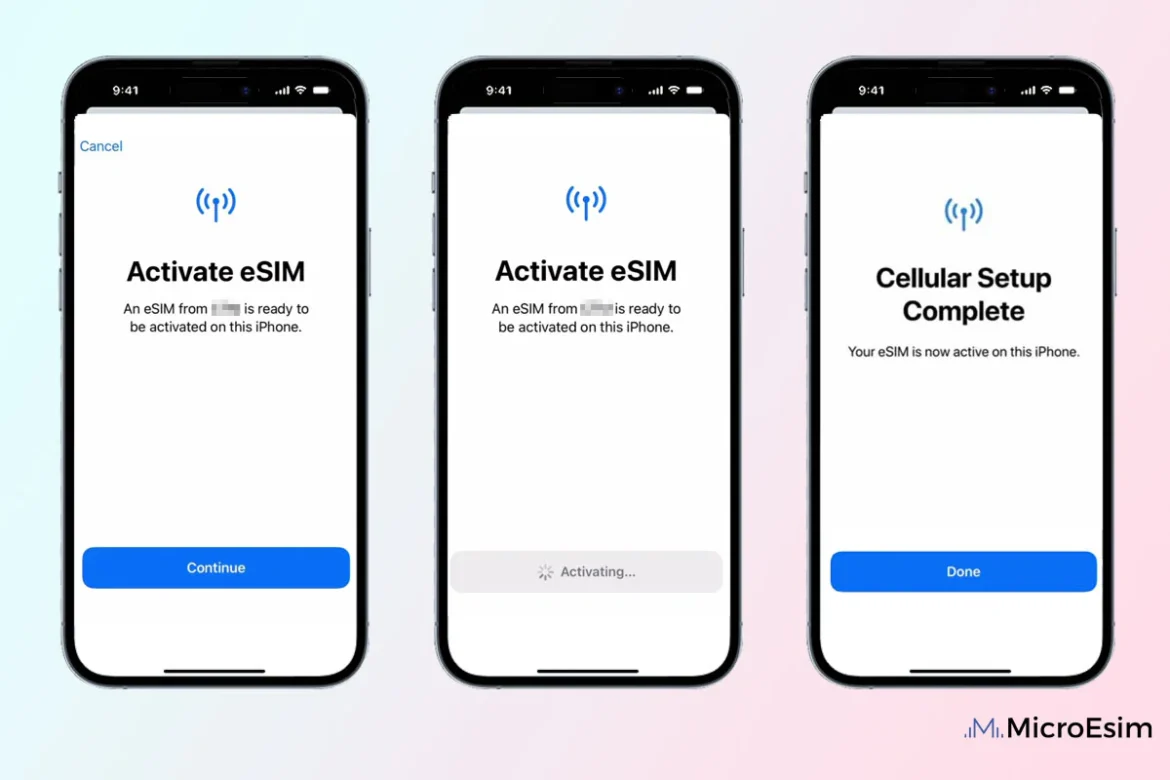
Activating eSIM on iPhone
Navigating to Cellular Settings
Open the cellular or mobile data section in settings and choose the option to add a cellular plan.
Using QR Code Activation
Scan the carrier-provided QR code when prompted.
Manual Activation Option
If QR scanning fails, manual entry of activation details may be available.
Labeling the eSIM
iPhones allow labeling plans for easier management, especially in dual SIM scenarios.
Managing Dual SIM With eSIM
Choosing Default Lines
Users can choose which SIM handles calls, messages, and mobile data.
Switching Between SIMs
Switching is instant and can be done through settings without restarting the device.
Data Usage Control
Each SIM profile tracks data usage independently, aiding cost control.
Transferring or Replacing eSIM Profiles
Changing Devices
Some carriers allow transferring eSIM profiles to new devices through account verification.
Deactivating Old Profiles
Old or unused profiles should be removed to avoid confusion or network conflicts.
Carrier Assistance
In some cases, carriers must reissue activation credentials.
Common Problems During eSIM Activation
QR Code Not Working
Blurry images, expired codes, or incorrect scanning angles can prevent recognition.
Activation Stuck or Failed
Network interruptions or server delays can cause partial activation.
No Signal After Activation
This may indicate incomplete provisioning or incorrect network settings.
Troubleshooting eSIM Activation Issues
Restarting the Device
A restart forces network re-registration.
Resetting Network Settings
This clears configuration conflicts without affecting personal data.
Re-adding the eSIM Profile
Deleting and re-downloading the profile often resolves setup errors.
Security and Privacy Considerations
eSIM Encryption
eSIM profiles are encrypted and protected by hardware-level security.
Loss or Theft Protection
eSIMs cannot be physically removed, reducing misuse risk.
Remote Deactivation
Carriers can remotely deactivate eSIMs if the device is lost.
eSIM for Business and Work Profiles
Separate Work Numbers
eSIM allows professionals to separate work and personal communication.
Corporate Device Management
Organizations can manage eSIM profiles remotely for employees.
Reduced Downtime
Quick profile changes reduce service interruptions.
eSIM and Future Smartphone Design
Trend Toward SIM-Free Devices
Manufacturers are increasingly moving toward eSIM-only designs.
Impact on Carriers
Carriers are adapting systems for digital provisioning.
User Experience Evolution
eSIM simplifies onboarding and network switching.
Preventing eSIM Activation Problems
Keep Software Updated
System updates improve compatibility and stability.
Store Activation Information Securely
QR codes and credentials should be saved until activation completes.
Avoid Frequent Profile Changes
Unnecessary switching increases error risk.
Understanding eSIM as a Connectivity Shift
Beyond Convenience
eSIM is not just a replacement for SIM cards, but a redesign of mobile connectivity.
Reduced Dependency on Physical Distribution
Digital provisioning improves accessibility.
Greater User Control
Users gain more flexibility over how and when they connect.
Conclusion
Activating eSIM on Android and iPhone represents a shift toward a more flexible, digital-first approach to mobile connectivity. While the absence of a physical SIM may initially feel unfamiliar, the underlying process is logical, secure, and efficient when understood correctly.
This guide has shown that eSIM activation is not a risky or complex operation, but a structured interaction between device, carrier, and network. By preparing properly, following the correct steps, and understanding how eSIM profiles work, users can activate and manage their mobile plans with confidence.
As smartphones continue to evolve, eSIM technology is becoming a standard rather than an exception. Learning how to activate and manage it today ensures readiness for a future where connectivity is faster, simpler, and entirely digital.