Overview Table
| Aspect | 2.4GHz Wi-Fi | 5GHz Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 2.4 gigahertz | 5 gigahertz |
| Coverage Range | Wider | Shorter |
| Wall Penetration | Strong | Weaker |
| Maximum Speed | Lower | Higher |
| Interference | High | Low |
| Device Compatibility | Very high | High (modern devices) |
| Ideal Use Case | Long range, basic tasks | High speed, low latency tasks |
| Congestion Level | Often crowded | Less crowded |
| Stability Over Distance | Better | Drops faster |
| Best Environment | Large homes, obstacles | Apartments, close-range use |
Introduction
Wireless 24GHz vs 5GHz internet has become the invisible backbone of modern life. From work and education to entertainment and communication, Wi-Fi enables constant connectivity across devices and environments. Yet behind this convenience lies a technical choice that significantly affects speed, reliability, and user experience: the Wi-Fi frequency band. The debate between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi is not about which is universally better, but about which is more suitable for specific situations.
Most modern routers support both bands, often labeled as dual-band or smart band routers. However, users frequently experience inconsistent speeds, dropped connections, or buffering without understanding that the issue may stem from using the wrong frequency for their environment or task. The choice between 24GHz vs 5GHz determines how far your signal travels, how fast data moves, and how resistant your connection is to interference.
This article examines 24GHz vs 5GHz Wi-Fi in depth. It explores their technical foundations, real-world performance, strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases. By combining narrative explanation, analytical comparison, and technical clarity, this guide aims to help you make informed decisions for home networks, offices, gaming setups, and smart homes.
Understanding Wi-Fi Frequency Bands
What a Frequency Band Means
A Wi-Fi frequency band refers to the range of radio waves used to transmit data wirelessly between a router and connected devices. These radio waves oscillate at specific frequencies, measured in gigahertz. The frequency determines how data travels through space, how much information it can carry, and how it interacts with physical obstacles.
Lower frequencies generally travel farther and penetrate obstacles more effectively. Higher frequencies carry more data but lose strength more quickly. This fundamental principle explains most of the differences between 24GHz vs 5GHz Wi-Fi.
Why Multiple Bands Exist
Early Wi-Fi standards relied heavily on the 2.4GHz band because it offered long range and acceptable performance with early hardware. As wireless usage increased, this band became congested. The introduction of the 5GHz band addressed the growing need for faster speeds, lower latency, and reduced interference.
Modern routers support both bands to balance coverage and performance. The challenge lies in selecting the right band for the right task.
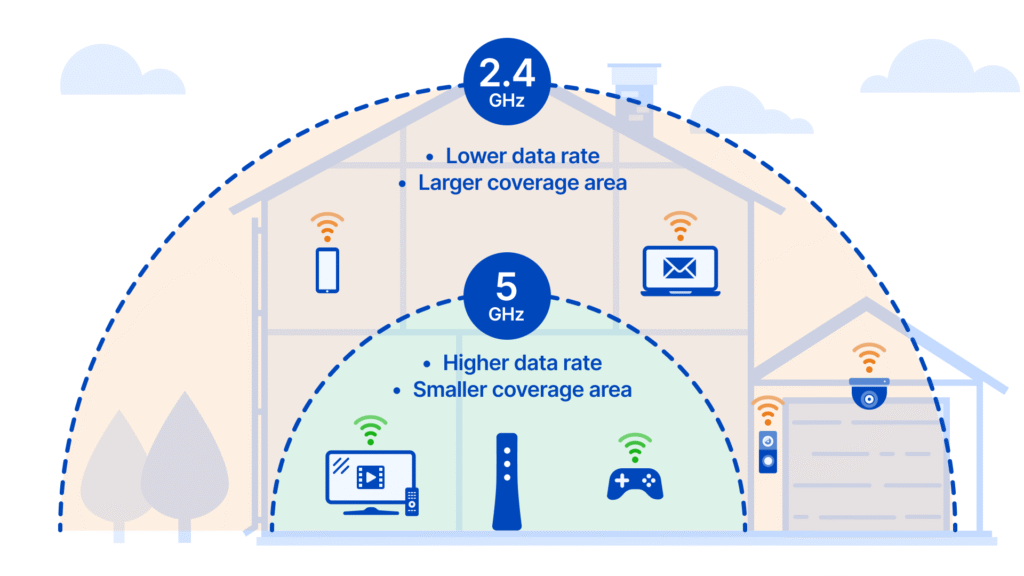
The 2.4GHz Wi-Fi Band Explained
Technical Characteristics
The 24GHz vs 5GHz band operates at a lower frequency, allowing radio waves to travel farther and pass through walls, furniture, and floors more effectively. This makes it highly suitable for larger spaces and multi-room coverage.
However, the band has limited available channels, many of which overlap. This overlap leads to interference, especially in densely populated areas where multiple networks operate simultaneously.
Strengths of 2.4GHz Wi-Fi
One of the primary advantages of 24GHz vs 5GHz Wi-Fi is its range. It maintains a usable signal even at long distances from the router. Devices located several rooms away or on different floors often remain connected more reliably on this band.
Compatibility is another major strength. Older smartphones, laptops, printers, and smart home devices often support only 2.4GHz. This makes it essential for mixed-device environments.
Limitations of 2.4GHz Wi-Fi
The 2.4GHz band is crowded. Many household devices such as Bluetooth accessories, cordless phones, baby monitors, and microwave ovens operate on the same frequency. This causes interference that can slow speeds and reduce stability.
Data transfer rates on 2.4GHz are also significantly lower compared to 5GHz. While sufficient for basic tasks like browsing and messaging, it struggles with high-bandwidth activities such as 4K streaming or large downloads.
The 5GHz Wi-Fi Band Explained
Technical Characteristics
The 5GHz band operates at a higher frequency, allowing it to carry more data at faster speeds. It offers a larger number of non-overlapping channels, which reduces congestion and improves performance consistency.
Because of its shorter wavelength, 5GHz signals weaken faster over distance and have more difficulty penetrating solid objects.
Strengths of 5GHz Wi-Fi
Speed is the defining advantage of 5GHz Wi-Fi. It supports significantly higher data rates, making it ideal for streaming high-resolution video, online gaming, video conferencing, and file transfers.
Lower interference is another key benefit. With more channels and fewer competing devices, 5GHz connections tend to be more stable in apartments and urban environments.
Latency is also lower, which is critical for real-time applications such as gaming and live collaboration.
Limitations of 5GHz Wi-Fi
The primary limitation of 5GHz Wi-Fi is range. Signal strength drops quickly with distance and physical barriers. A room or two away from the router, performance may decline noticeably.
Older devices may not support 5GHz, limiting its usefulness in some households. Additionally, outdoor or multi-floor coverage is less reliable compared to 2.4GHz.
Speed Comparison in Real-World Use
Theoretical vs Practical Speed
While manufacturers advertise high maximum speeds, real-world performance depends on environment, router quality, device capability, and interference. In practice, 5GHz consistently outperforms 2.4GHz at close range.
24GHz vs 5GHz delivers stable but modest speeds, suitable for everyday tasks. 5GHz provides faster downloads and smoother streaming, particularly when devices are close to the router.
Impact on Streaming and Downloads
High-definition and ultra-high-definition video streaming benefit greatly from 5GHz. Buffering is reduced, and playback remains stable even at higher bitrates.
Large file downloads complete significantly faster on 5GHz, saving time and reducing network congestion.
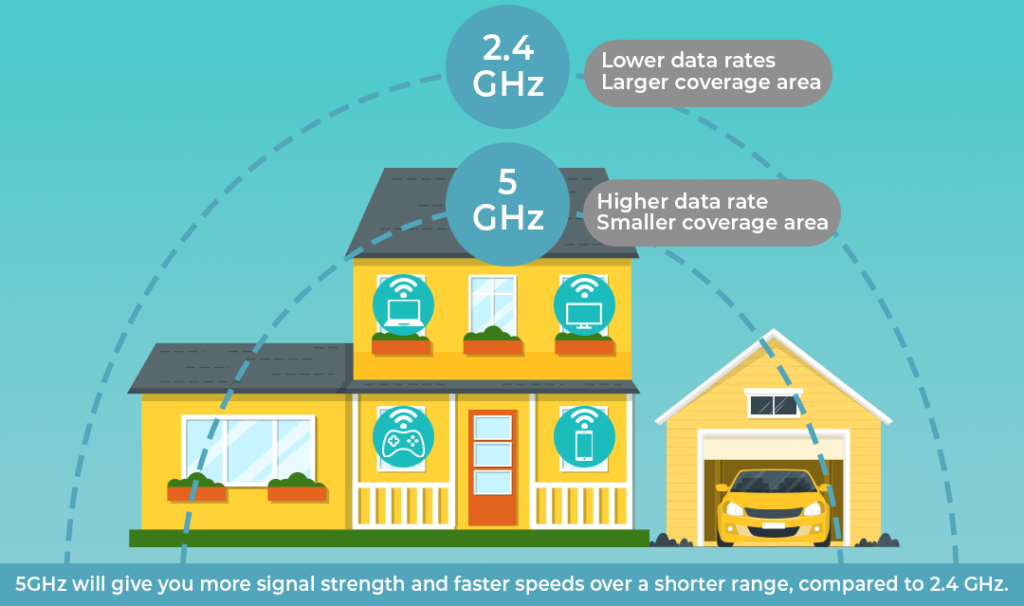
Range and Coverage Analysis
How Distance Affects Performance
24GHz vs 5GHz maintains usable speeds across greater distances, making it ideal for large homes or offices. It is more forgiving of walls and obstacles.
24GHz vs 5GHz excels in short-range scenarios. In the same room as the router, it delivers exceptional performance. Beyond that, signal degradation becomes noticeable.
Multi-Floor and Large Space Considerations
In multi-story buildings, 24GHz vs 5GHz often provides better vertical coverage. 5GHz may struggle unless supported by additional access points or mesh systems.
Interference and Network Stability
Sources of Interference
The 24GHz vs 5GHz band shares space with many common devices. This leads to fluctuating performance, especially during peak usage hours.
The 5GHz band experiences less interference due to fewer competing devices and more available channels.
Stability in Crowded Environments
In apartment complexes or office buildings, 5GHz offers superior stability. Its reduced congestion ensures consistent speeds and fewer drops.
Device Compatibility and Smart Homes
Legacy and Modern Devices
Many older devices support only 24GHz vs 5GHz. Smart home products such as bulbs, plugs, and sensors often rely on this band for compatibility and range.
Modern smartphones, laptops, and consoles support both bands, allowing users to choose based on performance needs.
Managing Mixed Networks
Dual-band routers allow simultaneous use of both frequencies. Smart band steering can automatically assign devices to the optimal band, balancing load and performance.
Gaming and Low-Latency Applications
Online Gaming Performance
24GHz vs 5GHz is preferred for gaming due to lower latency and higher speeds. It minimizes lag and packet loss during competitive play.
24GHz vs 5GHz may introduce higher latency, especially in congested environments, making it less suitable for fast-paced games.
Video Calls and Real-Time Work
Video conferencing and remote work benefit from the stability and speed of 5GHz when devices are close to the router.
Security and Reliability Considerations
Signal Leakage and Range
24GHz vs 5GHz signals travel farther, potentially extending beyond the intended area. While encryption protects data, wider coverage may increase exposure.
5GHz signals are more contained, reducing unintended reach and improving network control.
Consistency Over Time
24GHz vs 5GHz networks tend to maintain consistent performance due to lower interference. 2.4GHz may fluctuate depending on surrounding activity.
Router Placement and Optimization
Ideal Router Placement
Central placement improves coverage for both bands. Elevation and minimal obstructions enhance signal quality.
Using Both Bands Effectively
Assign high-bandwidth devices to 5GHz and low-bandwidth or distant devices to 2.4GHz. This maximizes overall network efficiency.
Choosing the Right Band for Your Needs
When 2.4GHz Is the Better Choice
24GHz vs 5GHz is ideal for large homes, devices far from the router, and basic internet activities. It is also essential for older and smart home devices.
When 5GHz Is the Better Choice
24GHz vs 5GHz is best for speed-critical tasks, gaming, streaming, and environments with heavy network congestion.
Using Both Together
Most users benefit from using both bands simultaneously. Dual-band routers are designed to provide flexibility rather than force a single choice.
The Future of Wi-Fi Bands
The evolution of Wi-Fi continues with newer standards introducing additional frequency bands and improved efficiency. While newer technologies expand options, 2.4GHz and 5GHz remain foundational to current wireless networking.
Their coexistence reflects a balance between range and performance, ensuring that diverse use cases are supported effectively.
Conclusion
The choice between 24GHz vs 5GHz Wi-Fi is not a matter of superiority but suitability. Each band serves a distinct purpose shaped by physics, technology, and real-world usage. The 2.4GHz band offers range, compatibility, and reliability across distance, while the 5GHz band delivers speed, low latency, and stability in close-range environments.
Understanding these differences empowers users to optimize their networks rather than rely on default settings. By aligning devices and activities with the appropriate frequency band, you can achieve faster speeds, fewer interruptions, and a more reliable wireless experience.
In an increasingly connected world, informed Wi-Fi choices transform everyday internet use from a source of frustration into a seamless and efficient experience.

